Almost anything that uses a motor or electricity to operate is built with magnets. That means cars also have them. In fact, magnets can be found in multiple places other than the motor in some cars. Unlike traditional automobiles, electric cars are powered by electricity rather than gas, so they have no tank. Instead, they have large batteries or fuel cells and “fueling up” is much like plugging into an outlet.
According to an analysis by the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg (ZSW), there were over 400,000 electric powered cars on the road in early 2014. Each of those requires magnetism to work. When it comes to electric cars, magnets are essential.
Electric motors and magnets
Magnets are a primary component in electric motors. In order to work they need to be made of a coil of wire that can spin and is encircled by strong magnets. Additionally, when an electric current is induced in the coil, it emits a magnetic field, opposing the magnetic field emitted by the strong magnets.
It follows the same attraction and repulsion rules of magnets. For instance, when you put the north and south poles of two separate bar magnets an invisible force will push them away from each other. The same concept occurs in motors, but they are modelled in a way that the repulsion is used to control an energy source.
This repulsion causes the coil to spin or rotate at a high speed. The coil is attached to an axle that allows the wheels to move. That is the basic model of an electric motor, but it is a more complex process.
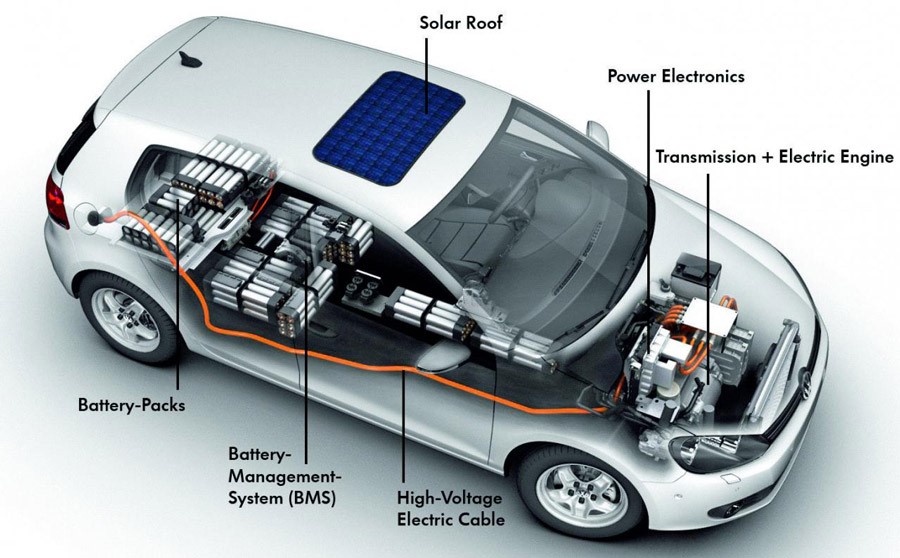
Below is a diagram briefing outlining the key components in an electric vehicle
Benefits:
- Cheaper to run – Electric vehicles have much lower running costs. The electricity to charge an electric vehicle works out around a third as much per kilometre as buying petrol for the same vehicle.
- Cheaper to maintain – Since having a lot less moving parts, electric vehicles prove easier and cheaper to maintain. No expensive exhaust systems, fuel injection systems or starter motors are needed.
- Less pollution – Electric vehicles help to reduce harmful air pollution from exhaust emissions.
- Safety improvements – Electric vehicles have a lower center of gravity that makes them less likely to roll over. Also, they are less likely to cause major fires or explosions and the durability of the vehicle body proves to make them safer in a collision.
- Less noise pollution – The engine is silent.
Drawbacks:
- Lack of consumer choice – The electric vehicles currently on the market consist mostly of compact pure electric cars and midsize plug-in hybrid sedans.
- Long refueling time – There are many issues surrounding the length of time it takes to refuel an electric vehicle. It usually takes around 4-6 hours to get fully charged.
- Higher cost – Electric vehicles are considerably more expensive than comparably equipped small to mid-sized gas-powered vehicle.
- Short driving range and speed – Electric vehicles are limited by range and speed. Most of these vehicles have range about 50-100 miles and need to be recharged again.
What does the future hold for electric vehicles?
Legislation throughout Europe has begun to force electric vehicles into the market, and it is expected that most of the world will follow suit. Therefore, leading to an even larger production of electric vehicles over the next few years.
Moreover, forecasts for electric vehicles over the next few years are being adjusted up dramatically as manufacturers in the automotive industry work furiously to develop electric vehicles with longer ranges to remain competitive in the market. However, some of these cars are a few years away due to the infrastructure needed to support the mass move from internal combustion engines to electric vehicles.
Goudsmit UK
At Goudsmit UK we sub-contract manufacture a vast variety of magnets and magnetic assemblies to suit your requirements. Contact us today for more information at info@goudsmit.co.uk or on +44 (0) 2890 271 001.
For more information download our products and services brochure.